In this tutorial, I will explain how by Group Policy (GPO) in an Active Directory environment, block the launch of programs and prevent the installation of certain software with the software restriction policy.
By default, if the users are not administrator (local) of the computer, it is not normally possible to install programs, on the other hand it is possible to launch portable applications which it downloads on Internet.
The group policy that I am going to present to you allows you to block this.
In addition to programs (EXE / MSI), group policy will allow us to block script execution (bat/powershell…).
To do this, we will rely on the software restriction policies found in the Security Settings.
Software Restriction Policies are available at the Computer Configuration and User Configuration levels, in the tutorial I will apply it at the Computer level.
Before implementing this type of strategy, I advise you to go through a test phase on an Organizational Unit, a bad configuration can block all programs.
To restrict the use of software, it is also possible AppLocker, on the other hand it is necessary to have Windows clients (10/11) enterprise or Windows Server.
Create Group Policy
In order to avoid any bad application of the group policy, we will create it in the Group Policy Objects container and then link it to the OU that we want to apply it.
I advise you to use this method for all your group policies.
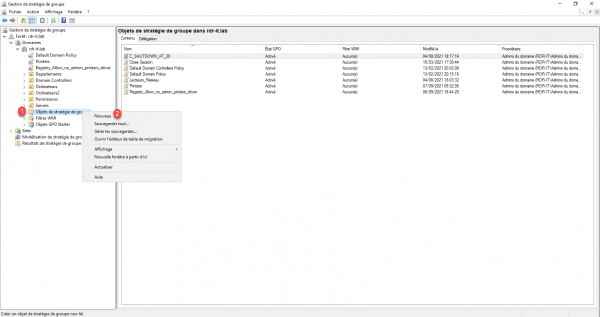
From the Group Policy Management console, right-click on the Group Policy Objects folder 1 click on New 2.
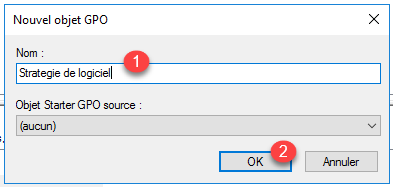
Name the group policy 1 then click on the OK button 2.
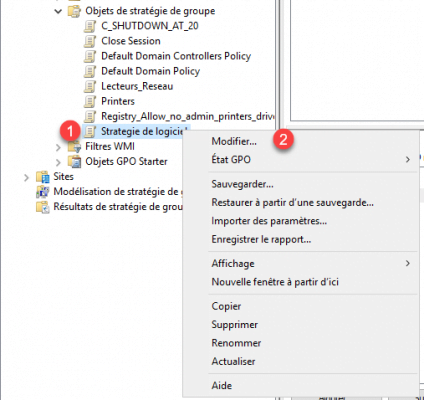
Right-click 1 on the object and click Modify 2.
Configuring Software Restriction Policy
From the Group Policy Management Editor, go to: Computer Configuration / Policies / Windows Settings / Security Settings / Software Restriction Policies 1.
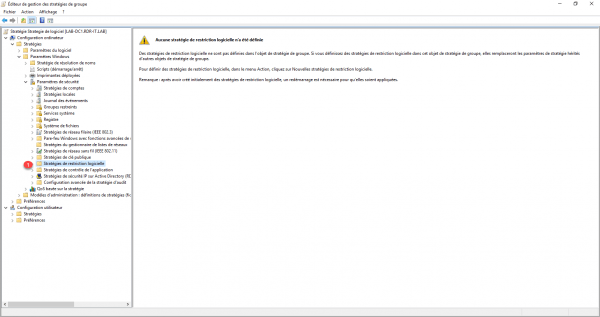
Right-click Software Restriction Policies 1 and click New Software Restriction Policies 2.
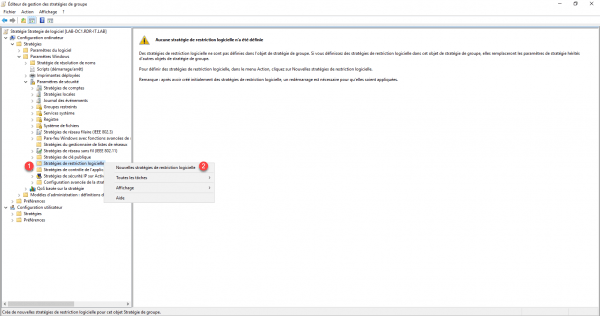
After clicking on New Software Restriction Policies, one can see that items have been added in the policy.
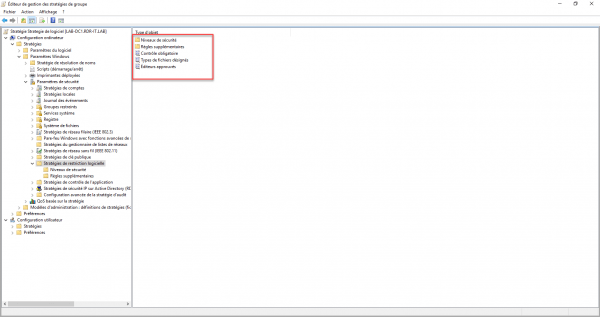
I will now explain how to configure the elements.
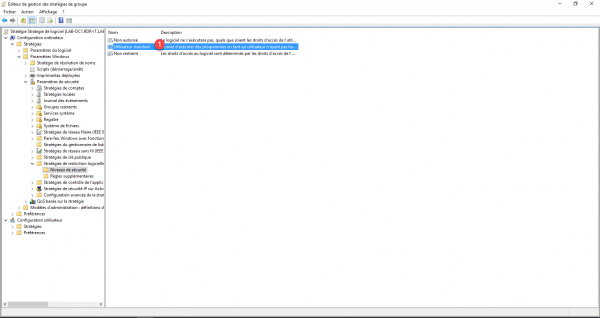
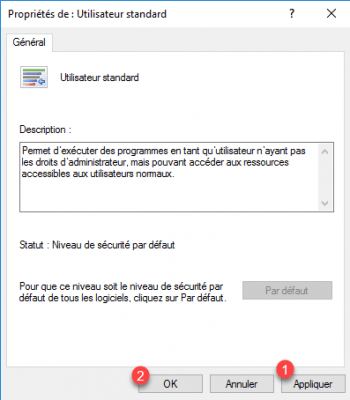
On security level 1, we find the behavior of the software restriction strategy, by default the configuration is unrestricted (you can see the selection at the bottom left of the icon). What we are going to do is switch to Standard User to activate the blocking.
Click on Standard User 1.
Click on the Default button 1.
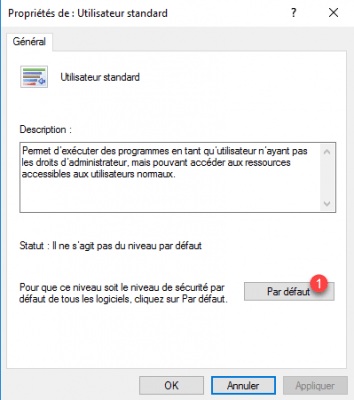
Validate the level change by clicking on Yes 1.
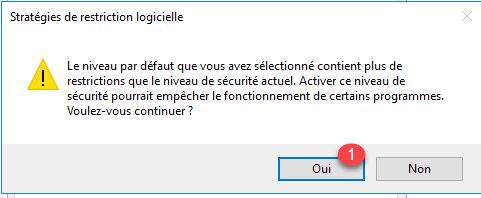
Validate the parameters by clicking on the Apply 1 and OK 2 buttons.
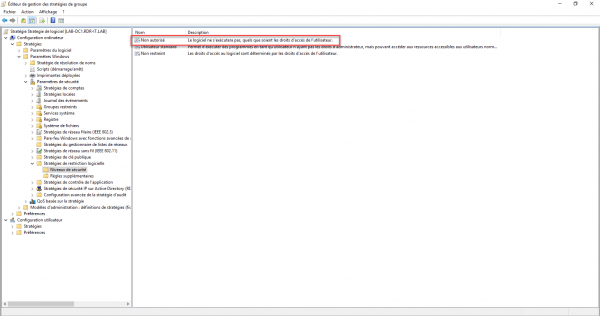
The level is now Unauthorized.
Go to the Additional Rules folder, here we can see that two exceptions have been created to allow the execution of programs in the C:\Windows and C:\Program Files folders.
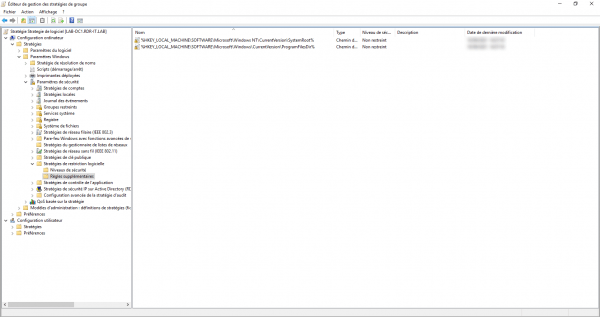
If you have problems launching programs during the tests, add the following paths:
– C:\Program Files (x86)
– C:\Program Files
– C:\Windows
Return to the Software Restriction Policies folder, we will continue to refine the configuration.
Click on Mandatory Control 1.
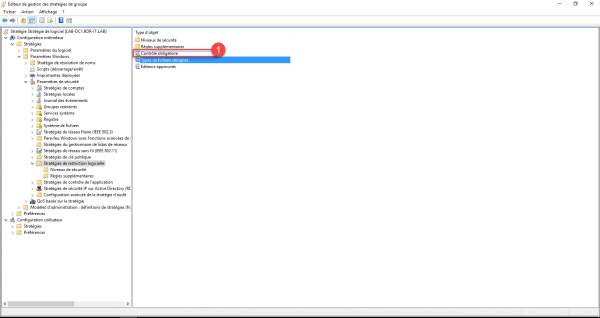
This property is used to exclude local administrators from policy 1.
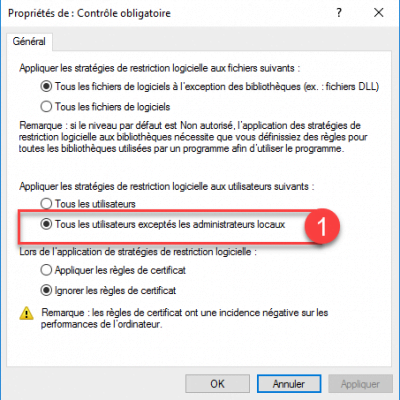
Then open the property: Designated File Types.
Here you can configure the extensions of the blocked files.
Group Policy is ready.
Link Group Policy to UO
Now all that remains is to link the group policy to the UO where it should apply.
Right-click the UO1 and click Link Existing GPO 2.
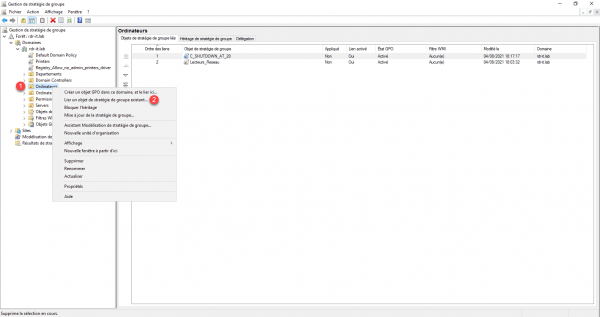
As a reminder, the strategy was configured at the Computer level, so I link the strategy to an UO that contains the computers.
Select Group Policy 1 and click OK 2.
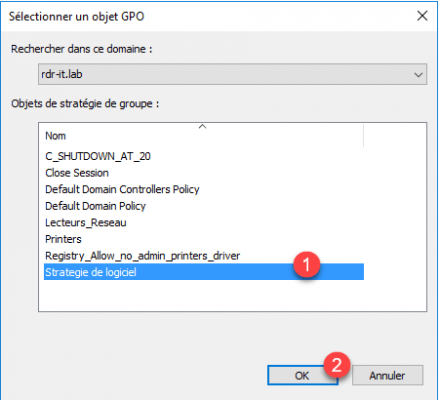
The strategy is linked to UO.
Test Software Restriction Policy
To test Group Policy, I’m going to use portable Firefox and test running it with an account that’s the computer’s local administrator and a domain user account. The Firefox executable will be on the desktop.
With the Administrator account, Firefox launches without problem:
With a standard user, the application is blocked:
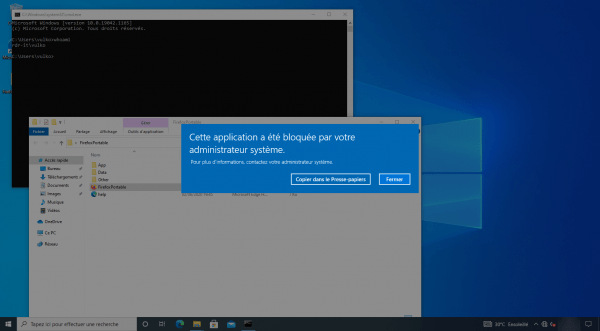
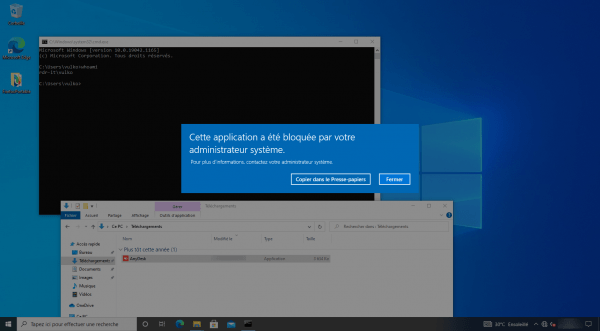
Still to illustrate the blocking, I downloaded AnyDesk from MS Edge and when I launch I also have the error message:
Conclusion
Through this software, you have seen how to block the execution and installation of software on computers.
This strategy allows to better control the programs, by preventing the execution of portable application and by blocking the installation, because certain software circumvents the lack of right of the user by installing the programs in the folder AppData of the user .
In business, it is also interesting to block remote control tools that could be used by service providers or users themselves.
It also increases the level of security by blocking the execution of scripts that could potentially be malicious.



Hello, interesting article.
as you surely already know, Google Chrome can be installed by domain users without priviledges.
I have tried a way to block this but i still cannot find a way.
If i implement this method in my domain, every applications will be blocked for installation? or only portable app ? and administrators will be still able to install programs?
thanks