Presentation
In this tutorial, we will see how to configure AppLocker in an Active Directory environment using group policies.
AppLocker is a Windows feature that is similar to a firewall at the application level.
AppLocker allows you to control the applications running on computers.
AppLocker is able to act on:
- Executables (.exe).
- Windows Installer (msi, msp …).
- The scripts.
- Application packaged (application store).
AppLocker acts through 3 possible conditions:
- Editor: which will allow you to configure information about the file (editor, version, etc.).
- Path: this condition defines the location of the file or the folders. The wildcard * is allowed.
- Hash the file.
AppLocker can be used in 2 ways:
- Audit mode: allows you to see the applications used, generally this mode is used before deployment.
- Apply mode: the rules are applied and the blocking effective.
As mentioned at the beginning, BitLocker acts as a firewall and therefore what is not explicitly authorized by a rule is blocked.
To illustrate the use of AppLocker in this tutorial, we will prohibit the execution of executable except the default locations Then to validate the proper functioning, we will launch putty.exe from the desktop of the user, which should be blocked by AppLocker.
As you can see, AppLocker allows you to increase the level of security by controlling the programs executed.
Personally, I find this solution very practical for blocking portable applications and also for preventing users from installing certain programs in their profile folder. (This method used by some software to bypass restrictions).
Prerequisites
AppLocker works on :
- Windows Server
- Windows 10 Enterprise
- Windows 10 Education
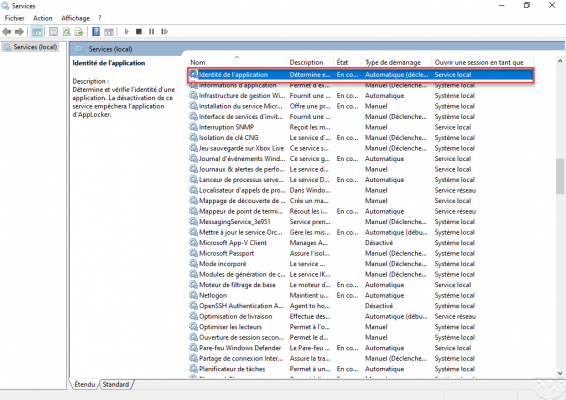
The Application Identity service (AppIDSvc) must be started.
Since Windows 10 and 2016, it is no longer possible to configure the AppIDSvc service via GPO.
You have to go through a script :
sc.exe config appidsvc start=autoor configure the service to start automatically on the image.In a deployment with MDT, it is possible to execute the command in the task sequence.
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/security/threat-protection/windows-defender-application-control/applocker/configure-the-application-identity-service
GPO : AppLocker configuration
To avoid applying the policy to Computers without fully configuring it, create a new Group Policy in the Group Policy Object container. Right click on the container 1 and click on New 2.
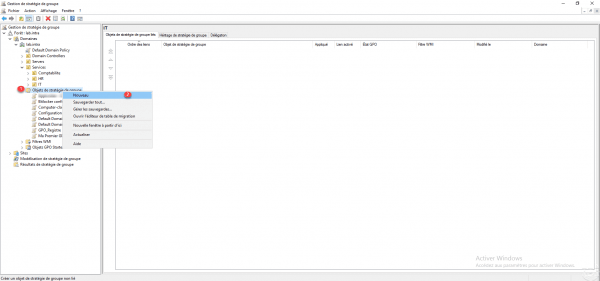
Name the group policy and click OK to create it.
Right click on the 1 group policy and click on Edit 2.
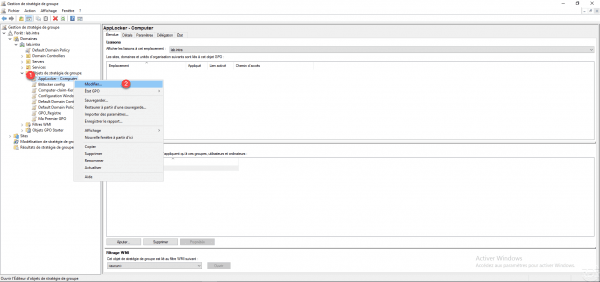
To access the settings for Applocker 1, go to the Computer configuration / Policies / Windows settings / Security settings / Application control policies location.
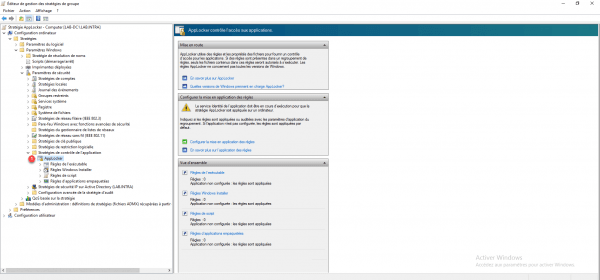
From the Applocker node, on the right-hand side is displayed an overview of the configuration and links to Microsoft documentation. By unfolding AppLocker you access the different element that AppLocker can “control”.
The first step is to create the default rules for each element that AppLocker can control, as a reminder once AppLocker is activated, anything that is not explicitly authorized is prohibited. Start the operation for Executable rule. Right click on it 1 and click on Create default rules 2.
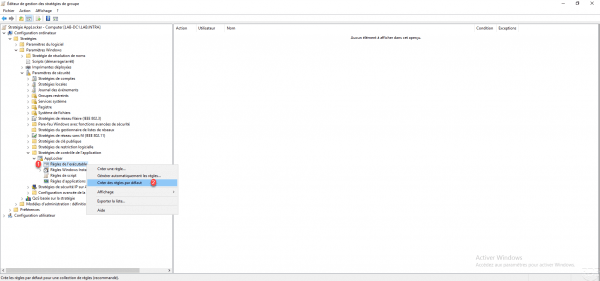
A default rule list is created 1.
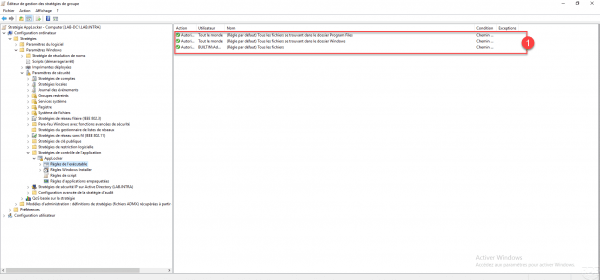
To add a custom rule, right-click in the central area then click on Create rule, just follow the wizard for creation.
Create the default rules for:
- Windows Installer
- Scripts
- Packaged app
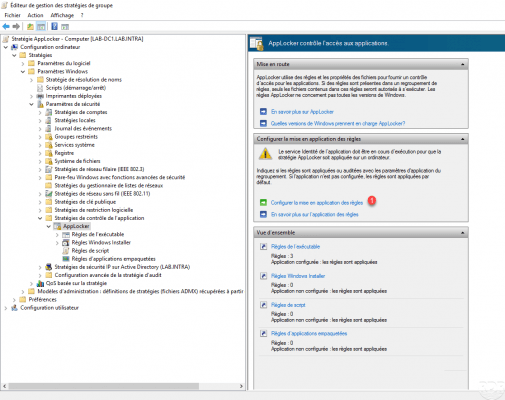
Return to the AppLocker node 1 and click on Configure the application of rules 2.
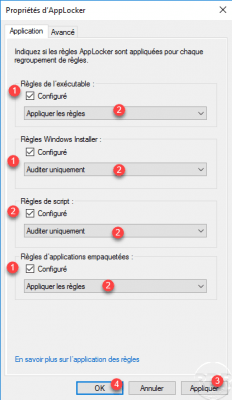
For each type of executable, check the Configured 1 box and choose on the rule is applied or audited 2, once configured click on Apply 3 and OK 4.
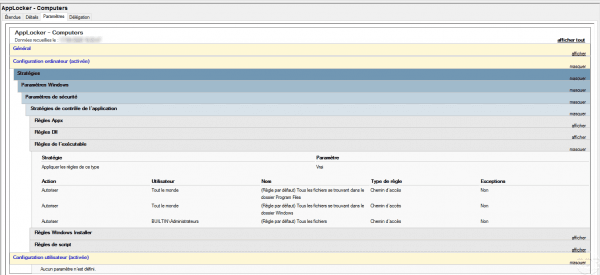
Close the Group Policy Editor, here is an overview of the settings for AppLocker:
Now that the strategy is ready, you have to link it to an OU.
Right click on the OU where the policy should be linked 1 and click on Link an existing group policy object 2.
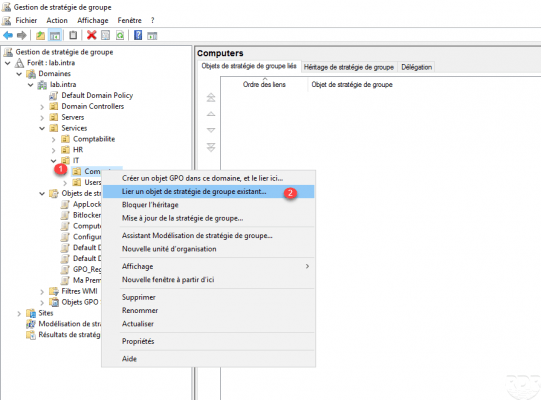
Select the strategy 1 and click on OK 2.
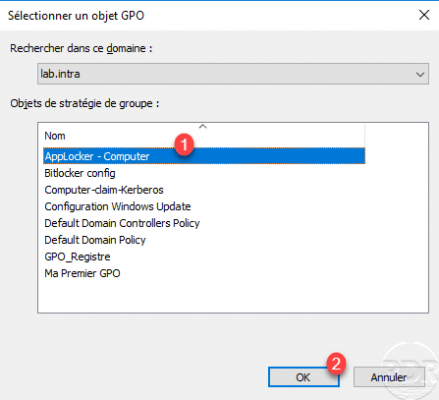
The policy is linked 1 and will be applied to Computer objects that depend on the OU.
Validate the functioning of AppLocker
On a computer where the policy applies, verify that the Application Identity service (AppIDSvc) is started.
To verify proper operation, download for example putty and launch it.
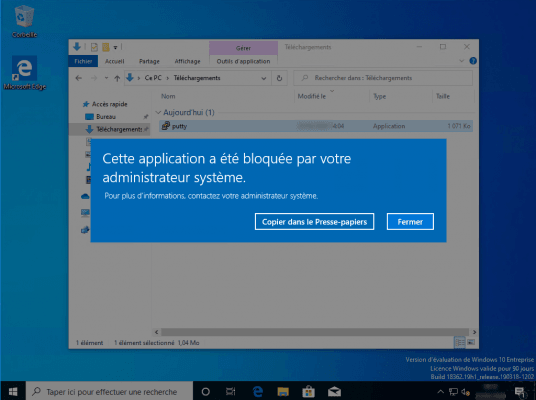
A warning message is displayed explaining that the application has been blocked.
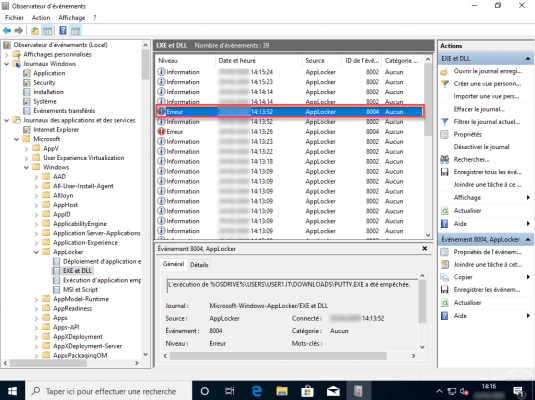
A trace is also added in the Windows event viewer with ID 8004. The AppLocker logs can be found in: Application and servide logs / Microsoft / Windows / AppLocker.
Conclusion
AppLocker is an easy-to-deploy security solution that increases the level of security by preventing unwanted applications from running.
In order to increase the security level of RDS servers, AppLocker is an easy solution to set up. For workstations, it is necessary to acquire Enterprise licenses.
Ressources complémentaires :