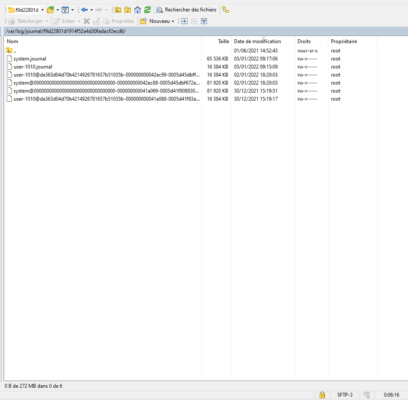
In this tutorial, we will see how to configure the size of systemd logs on an Ubuntu distribution.
By default, the logs located in the /var/log/journal folder can take several gigabytes of disk space.
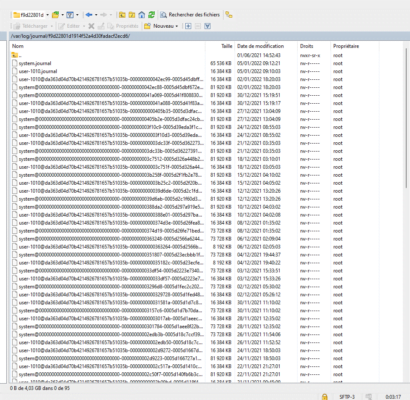
As can be seen from the screenshot below, the logs take up 4 Giga of disk space.
The configuration of the logs is done in the file /etc/systemd/journald.conf.
Here is the default file:
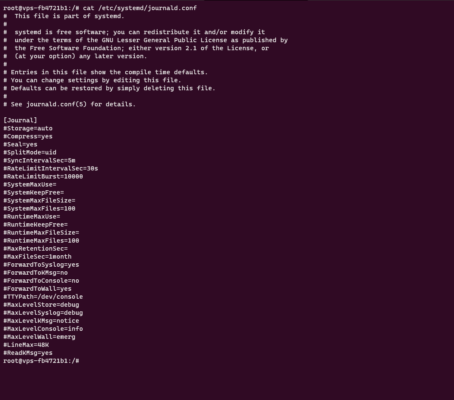
Open the file with nano for example:
sudo nano /etc/systemd/journald.confUncomment the SystemMaxUse line and set the desired maximum log size value.
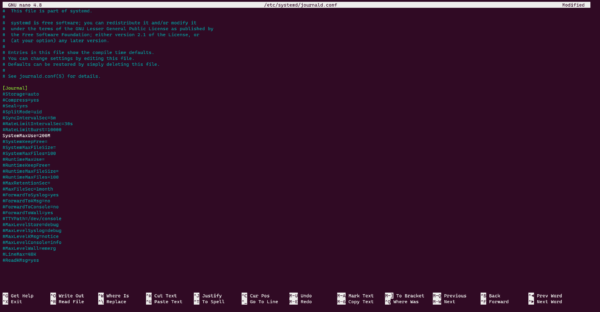
Here I indicated a maximum size of 200 Mo
Close saving changes.
Restart the daemon in charge of the systemd journal:
sudo systemctl restart systemd-journaldAfter the reboot, we can see that the logs are the size indicated and the rest has been deleted.