Presentation of NLB
Network Load Balancing (NLB) is a feature built into Windows that allows the implementation of load balancing at the network level. It is often used with IIS / FTP / RDS.
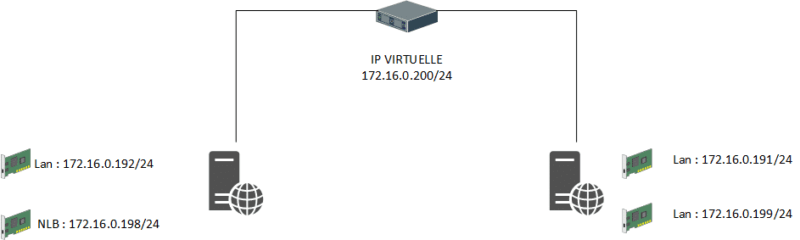
NLB works with a virtual IP address that is available to all hosts in the cluster.
NLB supports up to 32 nodes on the same cluster, according to Microsoft best practices it is advisable to create clusters of maximum 8 nodes.
The NLB feature relies on network-level distribution, one of the limitations of this solution is that the heatbeats tests monitor whether the hosts are online and not the service. If the web service of one of the hosts is non-functional but the host responds to the HB, requests will be sent to the host.
Representation of an NLB cluster in monodiffussion :
Prerequisites
Setting up a Network Load Balancing Cluster you need:
- At least two servers with the same service installed (for this lab I used two IIS web servers) and two network cards. A card will be for server management and a dedicated NLB cluster card. If the NLB cluster is configured in Multidiffussion it is not necessary to have two network cards.
- At least 3 IPs: 1 IP for the cluster that will be virtual and an IP address for each node
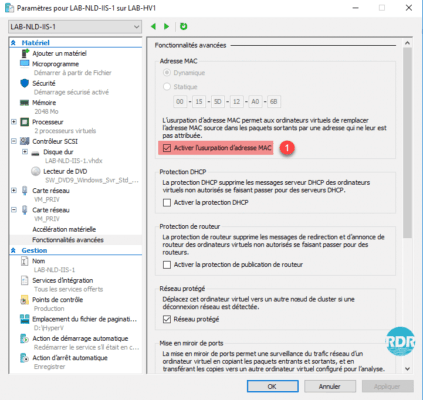
If your servers are under Hyper-V, you must activate the MAC address spoofing on network adapters dedicated to the NLB cluster.
Modes of transmission
Unicast: the default mode, it will disable the MAC address of the network card and replace it with an identical virtual address on all nodes.
Multicast: recommended mode, it can be used with one or more network cards. With this mode, the network adapter will have two MAC addresses, the one on the network adapter and the virtual MAC address of the cluster.
Installing NLB
The installation of the Network Load Balancing feature is to be done on each node of the cluster.
PowerShell
1. Open a PowerShell command prompt as an administrator and enter the following command to install the NLB role and administrative tools:
Install-WindowsFeature NLB,RSAT-NLB2. Wait during the installation.
3. Installation completed, close the PowerShell window.
Graphic mode
1. From the server manager, click Manage 1 / Add Roles and Features 2.
2. When launching the wizard, click Next 1.
3. Type of installation, choose Role-based or feature-based installation 1 and click Next 2.
4. Select the server 1 where NLB should be installed and click Next 2.
5. When selecting roles, click Next 1.
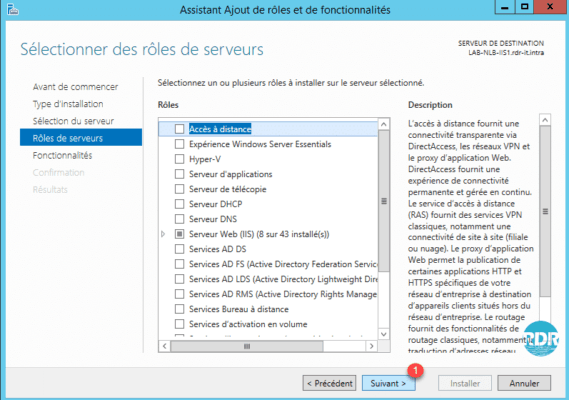
6. Features: Check Network Load Balancing 1.
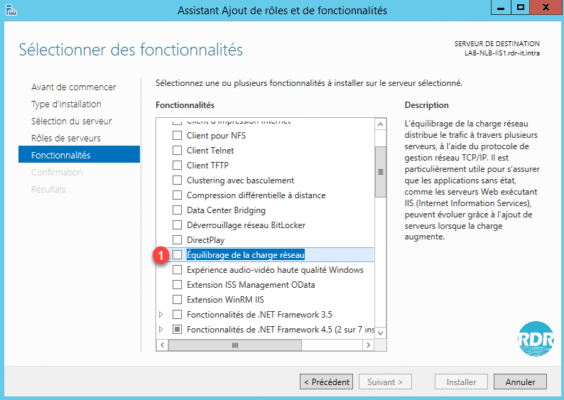
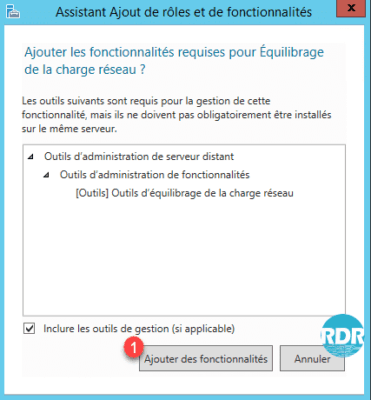
7. Click Add Features 1 to confirm the addition of dependencies.
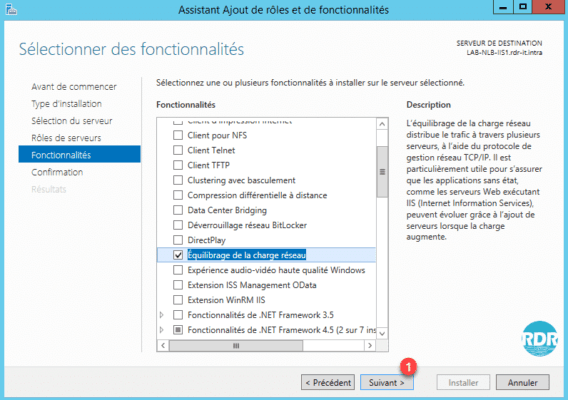
8. Click Next 1.
9. Confirm the installation by clicking Install 1.
10. Wait during the installation …
11. Installation completed, exit the wizard by clicking Close 1.
Unicast configuration
Setting up unicast network cards
The following operations are to be done on each server that will compose the cluster, the IP addresses are to be adapted according to your configuration.
1. Open the network connections and identify the cards.
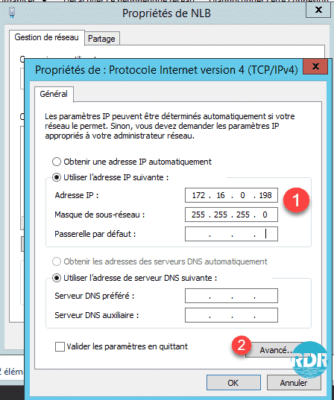
2. Go to the properties of the TCP / IPV4 protocol of the NLB network card and set its address 1 without setting Default Gateway and DNS server and click on Advanced … 2.
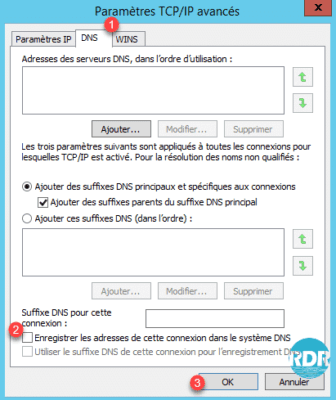
3. Go to the DNS 1 tab, uncheck the box 2 Save the addresses of this connection in the DNS system and click on OK 3 to validate the parameters.
4. Click OK to validate the IP address of the card.
Cluster creation
In this part, we will create the NLB cluster, which will initially consist of a single node.
1. Open the administration console.

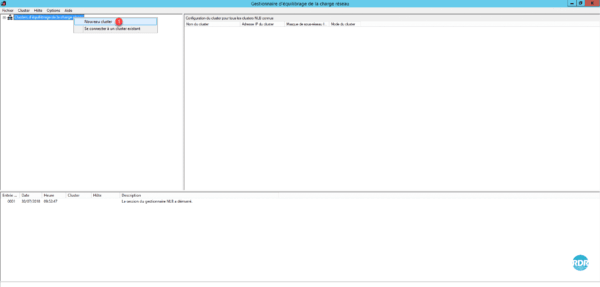
2. Right-click Network Load Balancing Clusters and click New Cluster 1.
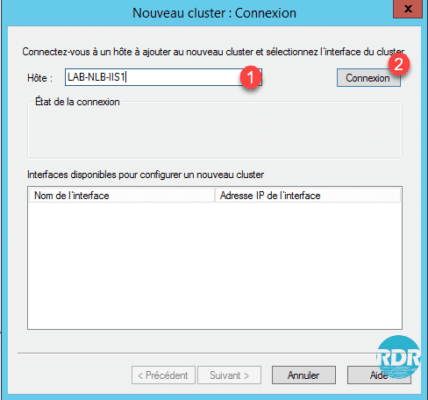
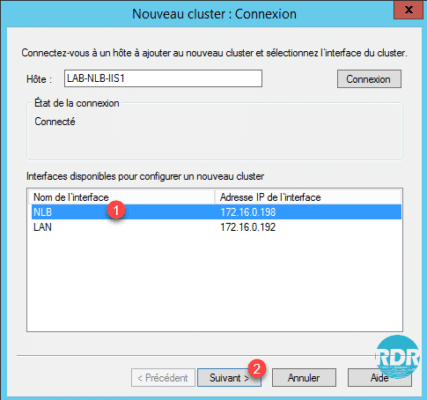
3. Enter the name of Host 1 and click on Connection 2.
4. Select the interface dedicated to cluster 1 and click Next 2.
5. Click Next 1.
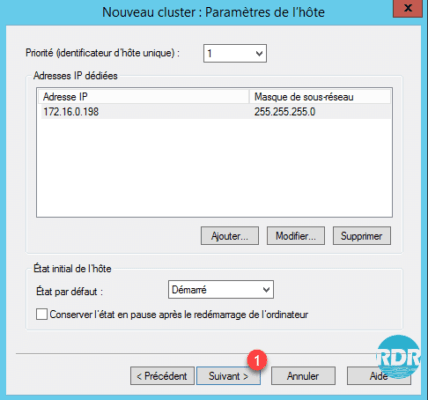
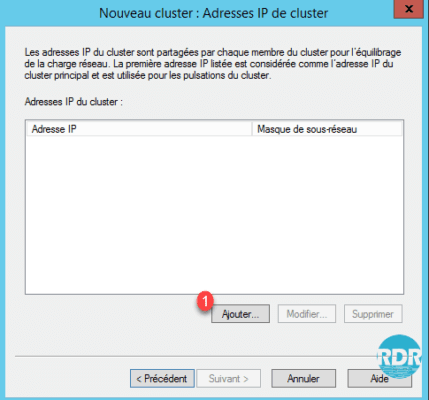
6. Click Add 1 to set a virtual address to the cluster.
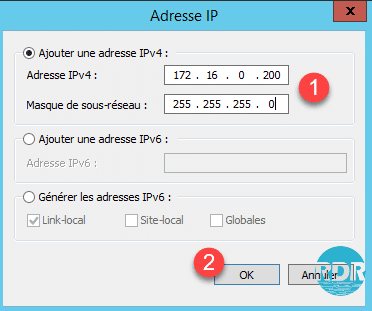
7. Enter the IPv4 Address and Subnet Mask 1 of the cluster and click OK 2.
8. Click Next 1.
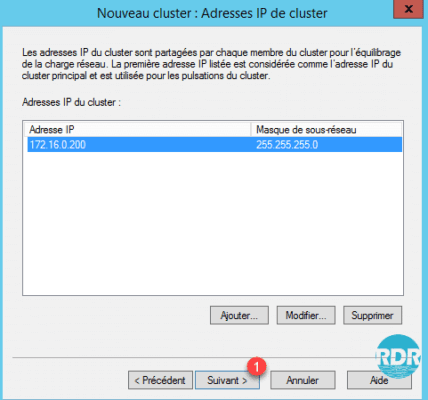
9. Enter the cluster name fqdn 1, select Unicast 2 and click Next 3.
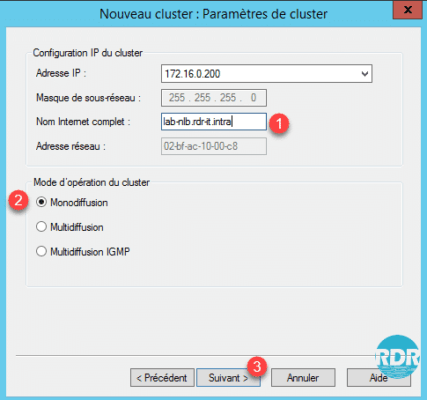
10. Click Edit … 1.
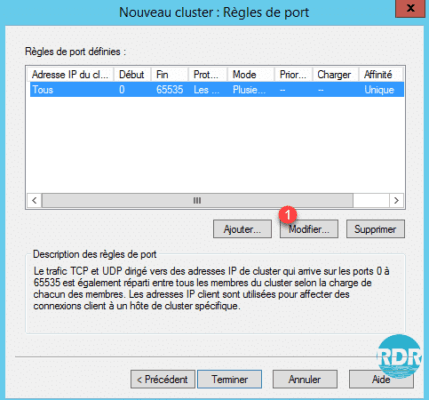
11. From this window it is possible to configure the cluster behavior:
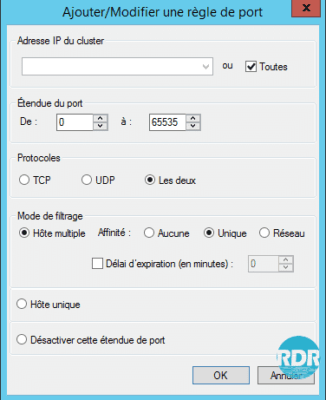
- Define the ports used
- Multiple Host (Active / Active) or Single Host (Active / Passive)
- Affinity:
- None: The connection will be sent to the host with the least connection, to use if no session is managed behind.
- Unique: The connection will always be sent to the same host (recommended)
- Network: Ability to manage the distribution according to the source network.
click OK or Cancel to close the window.
12. Click Finish 1 to create the cluster.
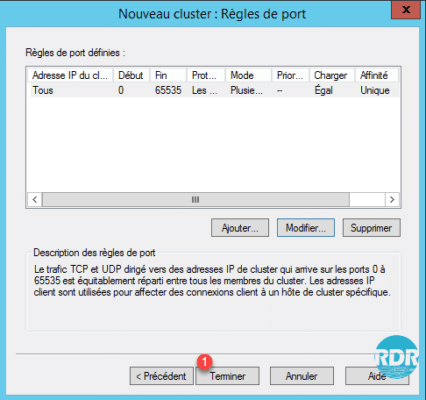
13. The cluster is being configured 1.
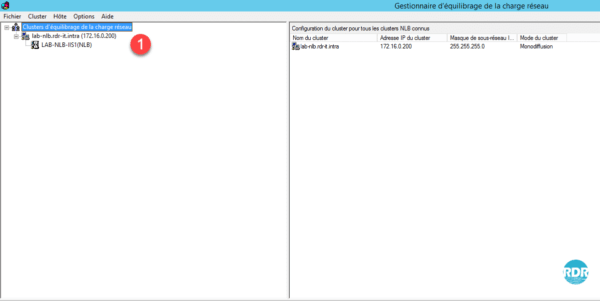
14. The node has changed to green 1, the NLB cluster is functional.
Configuration in Multicast mode
Multicast mode makes it possible to use hosts with only one network card and broadcast on the network.
Cluster creation
1. From the console, right-click Network Load Balancing Cluster 1 and click New Cluster 2 .
2. Enter the ip of node 1 and click on Connection 2 .
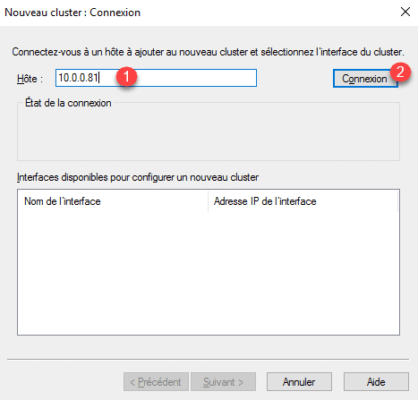
3. Once connected, select interface 1 and click Next 2 .
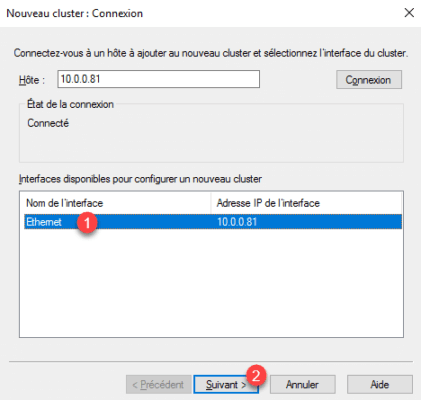
4. Click Next 1 .
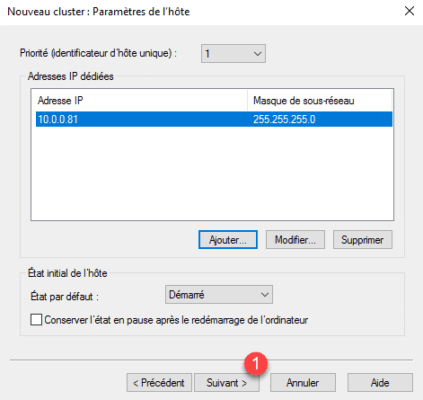
5. Click Add 1 to declare the IP address of the cluster.
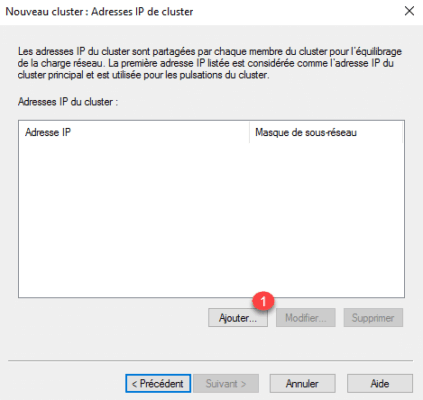
6. Enter the IP address 1 with the subnet mask 2 and click OK 3 .
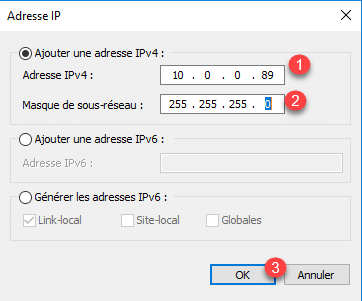
7. The added IP address 1 , click Next 2 .
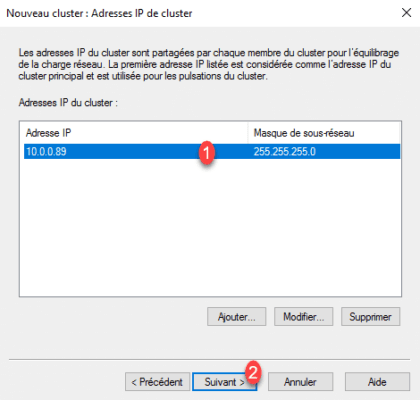
8. Enter the DNS name of cluster 1 , select Multicast mode 2 and click Next 3 .
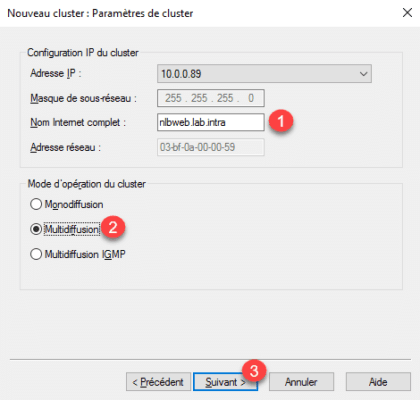
9. Configure port, by default all traffic is listened to. Click Finish 1 to create the cluster.
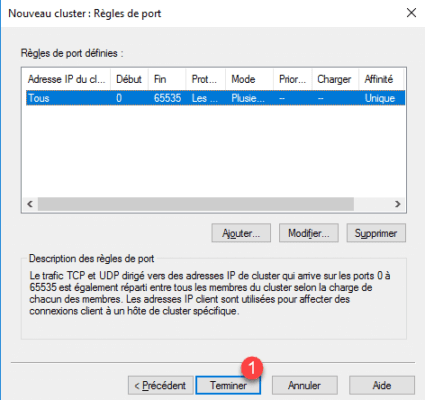
10. Wait while creating and configuring the NLB cluster.
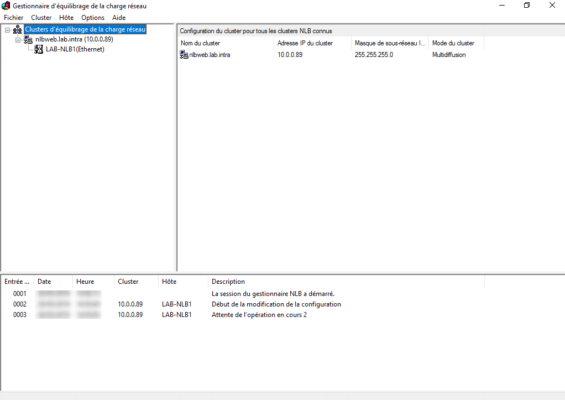
11. The cluster is created and the active node 1 .
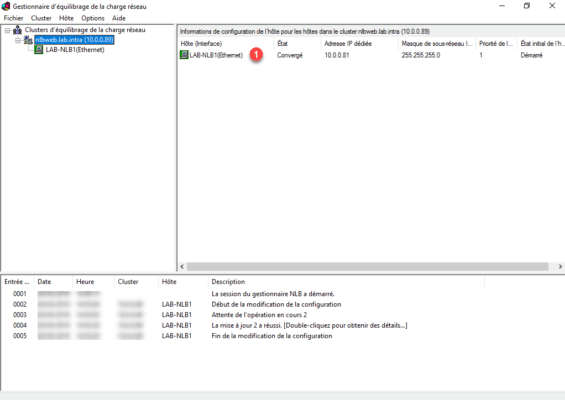
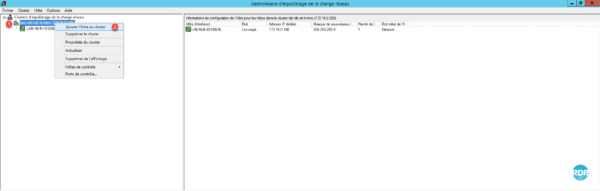
Adding a node to the cluster
1. From the Administration Console, right-click cluster 1 and click Add Host to Cluster 2.
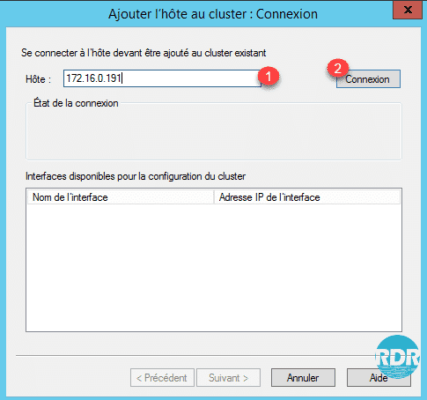
2. Enter the IP or Host Name 1 and click on Connection 2.
3. Select the NLB 1 interface and click Next 2.
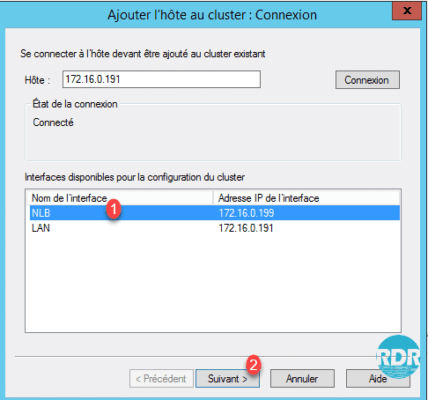
4. Click Next 1.
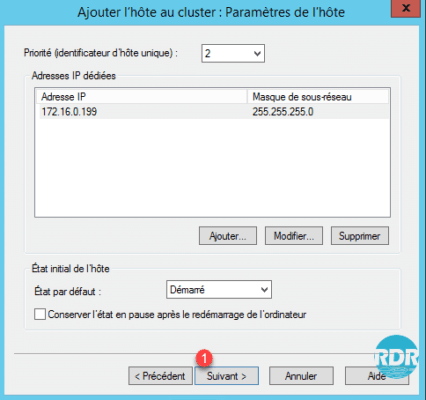
5. Click Finish 1.
6. Waiting during Host 1 enters the cluster.
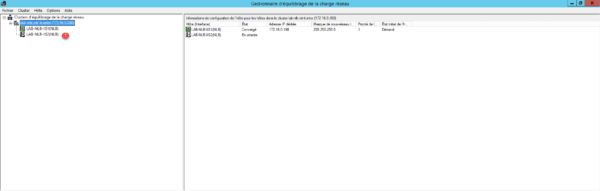
7. Both hosts are green 1.
You now have a highly available solution. To test from an IIS solution, simply put two different indexes on the sites and load the web page from different client.